Explore & Play
Discover interesting topics and solve the accompanying crossword puzzle.
European Crossword | Impact of Influential Figures in Europe
Table of Contents
Before diving into the content of this article, we invite you to engage with our European crossword. You can test your knowledge of iconic figures and their contributions to culture. If you’re unfamiliar with the topic, feel free to read the article first for some background, then return to enjoy the crossword for a fun way to reinforce what you’ve learned.
European Crossword
You can either fill in the crossword puzzle directly on this page or click the button in the bottom right corner to print it for free.

Cultural Icons: Artists and Thinkers Who Shaped Europe
Europe has been a cradle of culture, philosophy, and innovation, with countless individuals leaving indelible marks on history. From groundbreaking artists and literary giants to revolutionary thinkers and political leaders, these cultural icons have shaped European identity through their contributions. This article will explore the profound impact of these figures on various facets of European society. As you read, consider engaging with the accompanying crossword puzzle as a fun way to test your knowledge of these influential personalities.
I. Pioneers of Art: Shaping European Aesthetics
Art has always been a profound means of expression, reflecting the cultural, social, and political landscapes of its time. In Europe, numerous artists have emerged as pioneers, redefining aesthetics and influencing generations to come. This section will explore the masterpieces of painting and the evolution of music, highlighting the contributions of renowned figures such as Vincent van Gogh, Claude Monet, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.
A. The Masterpieces of Painting
1. Vincent van Gogh: Emotion in Color
Vincent van Gogh stands as one of the most influential figures in Western art history. His unique style, characterized by bold colors and expressive brushwork, captured the emotional essence of his subjects. Despite facing significant personal struggles, including mental health challenges, van Gogh’s work exudes a raw intensity that resonates with viewers. Paintings such as “Starry Night” and “Sunflowers” illustrate his ability to convey profound feelings through color and form.
Van Gogh’s use of color was not merely aesthetic; it was deeply symbolic. He believed that color could convey emotions and evoke feelings that words often could not. For instance, the vibrant yellows of his sunflowers reflect warmth and optimism, while the swirling blues and yellows of “Starry Night” evoke feelings of turbulence and wonder. His groundbreaking approach laid the foundation for modern art movements, encouraging artists to explore personal expression and the emotional impact of color.
2. Claude Monet: The Beauty of Light
Claude Monet, a leading figure in the Impressionist movement, revolutionized the way artists perceive and depict light. His commitment to capturing the transient effects of light on landscapes and everyday scenes marked a departure from traditional techniques. Monet’s series of paintings, such as “Water Lilies” and “Impression, Sunrise,” showcase his fascination with natural light and its changing qualities throughout the day.
Monet often painted en plein air, or outdoors, allowing him to directly observe the interplay of light and color in nature. This technique enabled him to depict scenes that felt alive and dynamic, reflecting the world as he saw it in fleeting moments. The Impressionist movement, with its emphasis on spontaneity and the effects of light, inspired countless artists to embrace new techniques and subject matter, fundamentally altering the trajectory of Western art.
B. The Evolution of Music
1. Ludwig van Beethoven: Breaking Boundaries
In the realm of classical music, Ludwig van Beethoven stands out as a transformative figure. His compositions marked the transition from the Classical era to the Romantic era, characterized by emotional depth and innovative structures. Beethoven’s symphonies, particularly his Fifth and Ninth, are celebrated for their dramatic intensity and thematic complexity.
Beethoven faced significant challenges, including progressive hearing loss, yet he continued to compose some of the most enduring music in history. His ability to convey profound emotions, from despair to triumph, resonates with listeners even today. His iconic “Ode to Joy,” found in the final movement of his Ninth Symphony, has become a universal anthem of hope and unity, illustrating the power of music to transcend barriers.
2. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart: The Gift of Melody
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart is often hailed as one of the greatest composers of all time. His prodigious talent was evident from a young age, and he produced an astonishing body of work that spans symphonies, operas, chamber music, and choral pieces. Mozart’s compositions, characterized by their melodic beauty and intricate harmonies, set new standards in classical music.
Mozart’s operas, such as “The Marriage of Figaro” and “Don Giovanni,” showcase his ability to blend music with drama, creating rich narratives that engage audiences emotionally. His skillful manipulation of musical form and structure laid the groundwork for future composers, influencing the development of opera and symphonic music. Mozart’s legacy endures, as his works remain staples in concert halls and operatic stages around the world.
The contributions of pioneers like Vincent van Gogh, Claude Monet, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart have profoundly shaped European aesthetics. Their innovative approaches and mastery of their respective mediums continue to inspire and influence artists and musicians globally. By exploring their masterpieces, we gain insight into the transformative power of art and music, which reflect the complexities of human experience and emotion.
II. Literary Giants: Voices that Resonate
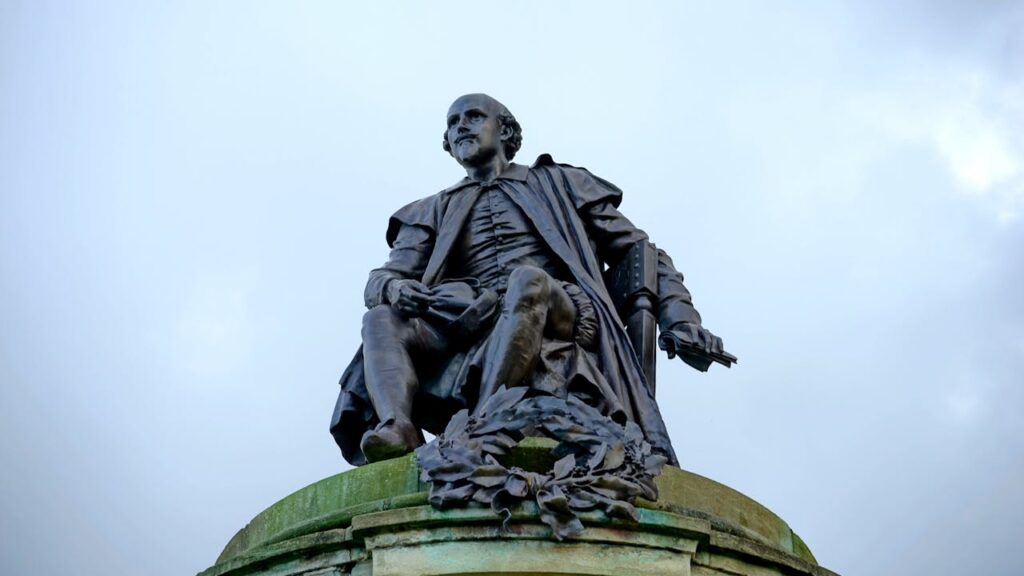
A. William Shakespeare: The Bard of Avon
1. The Timelessness of Shakespeare’s Works
William Shakespeare, often referred to as the Bard of Avon, is perhaps the most celebrated playwright and poet in the English language. His works encompass a vast range of genres, including tragedies, comedies, and histories, showcasing his exceptional ability to explore the depths of human emotion and the complexities of the human condition. Plays such as “Hamlet,” “Macbeth,” and “Romeo and Juliet” remain timeless classics, resonating with audiences for their exploration of themes like love, power, betrayal, and mortality.
Shakespeare’s use of language is unparalleled, blending poetic form with intricate character development. His mastery of iambic pentameter and inventive vocabulary has enriched the English language, introducing phrases and expressions still in use today. Moreover, his ability to create multifaceted characters, from the ambitious Lady Macbeth to the tragic Hamlet, allows readers to engage with their struggles and triumphs, fostering a deep emotional connection.
2. The Influence of Shakespeare on Modern Literature
The influence of Shakespeare extends far beyond his time, impacting countless writers, playwrights, and artists throughout the centuries. His exploration of universal themes, such as the nature of love and the consequences of ambition, resonates with audiences across cultures and eras. Contemporary adaptations of his works in film, theater, and literature demonstrate the enduring relevance of his themes and characters.
Moreover, Shakespeare’s innovative narrative techniques, including soliloquies and complex plots, have paved the way for modern storytelling. His ability to weave intricate subplots and develop characters with psychological depth has inspired writers like James Joyce and T.S. Eliot, who sought to explore the human experience through innovative narrative forms. Shakespeare’s legacy is not just found in his texts but also in the rich tradition of storytelling he has inspired across the globe.
B. Leo Tolstoy: A Voice of Conscience
1. The Depth of Human Experience in Tolstoy’s Novels
Leo Tolstoy, the Russian novelist and philosopher, is renowned for his profound explorations of morality, society, and the human spirit. His masterpieces, “War and Peace” and “Anna Karenina,” delve into the complexities of human relationships and the moral dilemmas faced by individuals within the constraints of society. Tolstoy’s ability to portray the breadth of human experience—from love and loss to redemption and moral conflict—has solidified his status as a literary giant.
In “War and Peace,” Tolstoy interweaves personal stories with the larger historical context of the Napoleonic Wars, examining the impact of war on individuals and society. His intricate characterizations allow readers to witness the internal struggles and transformations of characters such as Pierre Bezukhov and Natasha Rostova, making their journeys relatable and impactful. Similarly, “Anna Karenina” offers a poignant exploration of love and societal expectations, capturing the tragic consequences of choices made in the pursuit of happiness.
2. Tolstoy’s Philosophical Reflections
Beyond his narratives, Tolstoy’s philosophical reflections on morality and ethics have had a lasting influence on literature and thought. His later works, including “The Kingdom of God Is Within You,” explore themes of nonviolence, spiritual awakening, and the importance of compassion. These ideas have inspired social movements and thinkers worldwide, emphasizing the need for moral integrity and a deeper understanding of humanity.
Tolstoy’s writings encourage readers to confront the complexities of their own lives, challenging them to reflect on their values and relationships. His ability to weave profound philosophical insights into compelling narratives has left an indelible mark on literature, inspiring generations to seek deeper truths within themselves and society.
C. Virginia Woolf: A Trailblazer of Modernism
1. The Stream of Consciousness Technique
Virginia Woolf, a central figure in modernist literature, is celebrated for her innovative narrative techniques and exploration of the human psyche. Her novels, including “Mrs. Dalloway” and “To the Lighthouse,” employ the stream of consciousness technique, allowing readers to delve into the inner thoughts and emotions of characters in a fluid, non-linear manner. This approach challenges traditional storytelling conventions, inviting readers to experience the characters’ perceptions and reflections intimately.
Woolf’s exploration of time, memory, and identity reflects the complexities of modern life and the intricacies of human relationships. In “Mrs. Dalloway,” for instance, Woolf masterfully intertwines the thoughts of various characters, capturing the fleeting nature of time and the interconnectedness of their lives. Her ability to blend personal and social commentary within her narratives highlights the significance of individual experiences amidst the broader tapestry of society.
2. Feminism and the Role of Women in Woolf’s Works
Woolf’s contributions extend beyond narrative innovation; she is also a pivotal figure in feminist literature. In her essays, particularly “A Room of One’s Own,” Woolf advocates for women’s intellectual and creative freedom, emphasizing the importance of financial independence and personal space for female writers. Her reflections on the challenges faced by women in a patriarchal society resonate with contemporary discussions on gender equality and women’s rights.
Woolf’s characters often grapple with societal expectations and the constraints placed upon them, reflecting her own experiences as a woman in the early 20th century. Through her exploration of female identity and creativity, Woolf challenges readers to reconsider traditional gender roles and the barriers to self-expression. Her literary legacy continues to inspire writers and activists, fostering conversations about gender, identity, and the role of women in society.
D. Franz Kafka: The Absurdity of Existence
1. The Surreal World of Kafka’s Narratives
Franz Kafka, the Czech writer known for his surreal and often nightmarish narratives, delves into the absurdities of modern existence. Works such as “The Metamorphosis” and “The Trial” explore themes of alienation, bureaucracy, and the struggle for identity in an increasingly complex world. Kafka’s unique blend of the absurd and the mundane invites readers to confront the often surreal nature of human experience.
In “The Metamorphosis,” Kafka presents the shocking transformation of Gregor Samsa into a monstrous insect, a powerful metaphor for feelings of alienation and the burden of societal expectations. This startling premise challenges readers to consider the impact of isolation and the search for meaning in a world that can feel indifferent and oppressive. Kafka’s exploration of existential themes resonates deeply with contemporary audiences grappling with similar feelings of disconnection.
2. The Influence of Kafka on Modern Literature
Kafka’s influence extends far beyond his lifetime, impacting a diverse array of writers and thinkers across various fields. His exploration of the absurd has inspired existentialist philosophy and literature, with authors like Albert Camus and Jean-Paul Sartre drawing on Kafka’s themes to explore the human condition. The term “Kafkaesque” has become synonymous with situations that evoke the sense of helplessness and absurdity found in his works.
By grappling with the complexities of existence and the often surreal nature of reality, Kafka encourages readers to reflect on their own experiences and the societal structures that shape their lives. His ability to articulate the anxieties of the modern world has solidified his place as a literary giant whose works continue to resonate and inspire critical thought.
The voices of literary giants like William Shakespeare, Leo Tolstoy, Virginia Woolf, and Franz Kafka have left an indelible mark on the cultural landscape of Europe. Through their innovative storytelling, profound insights, and exploration of the human experience, they have shaped the way we understand ourselves and our world. Their works continue to inspire new generations of readers, reminding us of the power of literature to challenge, resonate, and connect us across time and space.
III. Philosophical Foundations: Ideas that Shaped Societies
A. Socrates: The Father of Western Philosophy
1. The Socratic Method and Its Legacy
Socrates, often regarded as the father of Western philosophy, introduced a dialectical method of inquiry that has had a profound impact on education and critical thinking. His approach, known as the Socratic Method, involves asking a series of probing questions to stimulate critical thinking and illuminate ideas. This method not only challenges individuals to examine their beliefs and assumptions but also fosters a culture of dialogue and intellectual exploration.
Socrates’ emphasis on questioning and self-examination laid the groundwork for subsequent philosophical inquiry. His famous assertion that “the unexamined life is not worth living” underscores the importance of introspection and ethical reflection. This principle remains central to contemporary education and philosophical practice, encouraging individuals to engage in critical dialogue about fundamental questions concerning morality, existence, and the nature of knowledge.
2. Ethics and the Pursuit of Virtue
At the heart of Socratic philosophy is the pursuit of virtue and the belief that knowledge leads to righteous action. Socrates posited that if individuals truly understood what is good, they would act accordingly. This idea challenges us to consider the relationship between knowledge, ethics, and behavior, prompting ongoing discussions about moral responsibility and the nature of a virtuous life.
Socrates’ legacy extends beyond his immediate context; his ideas have influenced countless philosophers and ethical theorists throughout history. His commitment to ethical inquiry has paved the way for discussions on virtue ethics, which continue to shape contemporary debates about morality and the good life.
B. Immanuel Kant: The Architect of Modern Philosophy
1. The Categorical Imperative and Moral Philosophy
Immanuel Kant, a central figure in the Enlightenment, revolutionized moral philosophy with his concept of the Categorical Imperative. This principle posits that moral actions must be universally applicable; in other words, individuals should act according to maxims that could be consistently willed as universal laws. Kant’s emphasis on rationality and autonomy laid the foundation for modern ethical theories, challenging individuals to consider the moral implications of their actions.
Kant’s approach emphasizes the importance of human dignity and respect for individuals as rational agents. His belief in the inherent worth of each person has had far-reaching implications for discussions on human rights and social justice, influencing movements advocating for equality and ethical treatment across various spheres of life.
2. The Impact of Kant’s Ideas on Politics and Society
Beyond ethics, Kant’s contributions extend to political philosophy, where he advocated for ideas of freedom, democracy, and the rule of law. His vision of a cosmopolitan world order, rooted in the principles of justice and mutual respect, resonates in contemporary discussions on international relations and global governance.
Kant’s emphasis on the importance of reason and autonomy has also influenced modern concepts of citizenship and civic responsibility. His writings encourage individuals to engage actively in shaping their societies and to pursue a moral framework that upholds the dignity and rights of all individuals.
C. Friedrich Nietzsche: The Critique of Traditional Values
1. The Concept of the Übermensch
Friedrich Nietzsche, known for his provocative and often controversial ideas, challenged the foundations of traditional morality and religion. His concept of the Übermensch, or “Overman,” represents an individual who transcends societal norms and creates their own values. Nietzsche’s critique of conventional morality encourages readers to question established beliefs and embrace a more authentic existence.
Nietzsche’s proclamation that “God is dead” reflects his rejection of metaphysical explanations and his call for individuals to forge their own paths in a world devoid of absolute truths. This radical perspective resonates with contemporary existentialist thought, urging individuals to confront the absurdity of existence and find meaning in their own choices.
2. The Will to Power and Its Implications
Central to Nietzsche’s philosophy is the concept of the “will to power,” which he viewed as a fundamental driving force in human behavior. This idea emphasizes the desire for growth, mastery, and self-overcoming, challenging individuals to pursue their potential and embrace creativity. Nietzsche’s emphasis on individualism and self-actualization has inspired a diverse range of thinkers and artists, encouraging them to explore new forms of expression and challenge societal conventions.
Nietzsche’s influence extends to discussions on ethics, psychology, and culture, prompting debates about the nature of morality in a post-religious world. His ideas encourage individuals to embrace their instincts and passions, paving the way for a more authentic and fulfilling life.
D. Simone de Beauvoir: Feminism and Existentialism
1. The Second Sex and the Construction of Gender
Simone de Beauvoir, a prominent existentialist philosopher and feminist, made significant contributions to discussions on gender, identity, and the human condition. In her groundbreaking work, “The Second Sex,” de Beauvoir explores the construction of femininity and the societal structures that have historically marginalized women. Her famous assertion that “one is not born, but rather becomes, a woman” underscores the notion that gender identity is shaped by cultural and social influences.
De Beauvoir’s analysis of women’s oppression and her call for liberation have had a profound impact on feminist thought. Her exploration of the interplay between gender and existential freedom encourages individuals to challenge societal norms and strive for equality, making her a pivotal figure in the feminist movement.
2. Existential Freedom and Responsibility
Beyond her feminist contributions, de Beauvoir’s existentialist philosophy emphasizes the importance of personal freedom and responsibility. She argues that individuals must confront the challenges of existence and take ownership of their choices. This perspective aligns with existentialist themes of authenticity and self-definition, urging individuals to engage actively in their lives and relationships.
De Beauvoir’s ideas have resonated with contemporary discussions on gender, identity, and autonomy. Her emphasis on the importance of recognizing and challenging oppressive structures continues to inspire movements advocating for social justice and equality, making her a crucial voice in both philosophy and feminism.
The philosophical foundations laid by figures like Socrates, Immanuel Kant, Friedrich Nietzsche, and Simone de Beauvoir have profoundly shaped European societies and continue to influence contemporary thought. Their explorations of ethics, identity, freedom, and the nature of existence encourage individuals to engage in critical reflection and dialogue, fostering a deeper understanding of ourselves and the world around us. As we grapple with complex societal issues, the insights of these philosophers remind us of the importance of philosophical inquiry in navigating the challenges of modern life.
IV. Political Icons: Leaders of Change
A. Winston Churchill: The Resilient Leader
1. Leadership During Adversity
Winston Churchill, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom during World War II, is celebrated for his indomitable spirit and exceptional leadership during one of history’s darkest periods. Churchill’s ability to inspire hope and resilience in the face of adversity played a crucial role in rallying the British people against the Nazi regime. His famous speeches, characterized by their stirring rhetoric and unwavering resolve, galvanized public support and fostered a sense of unity during a time of crisis.
Churchill’s strategic foresight and commitment to victory were instrumental in the Allied forces’ success. He recognized the importance of international collaboration and worked tirelessly to build alliances with other nations, emphasizing the need for collective action against tyranny. His leadership style, marked by determination and courage, continues to serve as a model for effective crisis management and public service.
2. The Legacy of Churchill’s Vision
Beyond the battlefield, Churchill’s vision for post-war Europe emphasized the need for unity and cooperation among nations. He was an early advocate for European integration, believing that collaboration would prevent future conflicts and promote stability. His famous “Iron Curtain” speech in 1946 highlighted the necessity of standing against totalitarianism and fostering democratic values.
Churchill’s legacy as a political icon extends beyond his wartime leadership; his ideas about governance, democracy, and international relations continue to influence contemporary political discourse. His unwavering commitment to freedom and resilience serves as a reminder of the importance of strong leadership in times of crisis.
B. Angela Merkel: The Steadfast Chancellor
1. A New Era of Leadership
Angela Merkel, Germany’s first female Chancellor, served from 2005 to 2021, leading the country through significant challenges and transformations. Known for her pragmatic approach and steady leadership style, Merkel played a crucial role in guiding Germany and Europe through economic crises, refugee issues, and evolving global dynamics.
Merkel’s leadership during the Eurozone crisis showcased her commitment to stability and economic growth. She advocated for fiscal responsibility while also recognizing the need for solidarity among European nations. Her ability to balance national interests with a broader European vision underscored her role as a key figure in fostering unity within the European Union.
2. Merkel’s Impact on Global Politics
Merkel’s influence extended beyond Germany; she emerged as a leading voice on global issues such as climate change, migration, and international security. Her advocacy for environmental sustainability and commitment to multilateralism positioned Germany as a key player on the global stage.
As a role model for women in leadership, Merkel’s tenure has inspired a new generation of female leaders. Her emphasis on rational decision-making, consensus-building, and inclusivity serves as a blueprint for effective governance in a rapidly changing world.
C. Margaret Thatcher: The Iron Lady
1. Transforming the British Economy
Margaret Thatcher, the United Kingdom’s first female Prime Minister, is renowned for her transformative policies and strong leadership. Serving from 1979 to 1990, she implemented a series of economic reforms that reshaped British society. Known as “Thatcherism,” her approach emphasized free-market principles, deregulation, and privatization of state-owned industries.
Thatcher’s leadership style was marked by decisiveness and unwavering conviction. Her commitment to reducing government intervention in the economy was met with both support and opposition, but her policies ultimately contributed to revitalizing the British economy during a period of stagnation.
2. The Global Influence of Thatcher’s Policies
Thatcher’s influence extended beyond the UK; her policies had a significant impact on global economic trends. She championed neoliberalism, advocating for market-oriented reforms and limited government intervention. This approach resonated with leaders in other countries, paving the way for similar policies worldwide.
Despite the controversies surrounding her leadership, Thatcher’s legacy as a political icon endures. Her emphasis on individual responsibility, entrepreneurship, and economic freedom continues to influence discussions on governance and economic policy.
Political leaders like Winston Churchill, Nelson Mandela, Angela Merkel, and Margaret Thatcher have left an indelible mark on European history and global affairs. Their commitment to change, resilience in the face of adversity, and vision for a better future continue to inspire new generations of leaders and activists. As we reflect on their legacies, we are reminded of the power of leadership to shape societies and foster progress in an ever-evolving world.
V. Innovators and Inventors: Crafting the Future
The annals of European history are rich with the contributions of innovators and inventors whose groundbreaking ideas and inventions have shaped not only the continent but the world at large. This section explores the lives and achievements of notable figures such as Nikola Tesla, Marie Curie, Johannes Gutenberg, and Thomas Edison, highlighting how their ingenuity and creativity have paved the way for advancements in various fields, from science and technology to arts and industry.
A. Nikola Tesla: The Visionary Engineer
1. Revolutionizing Electrical Engineering
Nikola Tesla, a Serbian-American inventor and electrical engineer, is best known for his pioneering work in the development of alternating current (AC) electricity. Born in 1856 in what is now Croatia, Tesla’s innovative ideas about electrical power transmission and electromagnetism revolutionized how electricity is generated and distributed. His invention of the Tesla coil, a high-voltage transformer, laid the groundwork for wireless transmission of energy.
Tesla’s visionary concepts extended beyond practical engineering. He envisioned a future where electricity would be freely available to all, empowering humanity and transforming daily life. His ambition to harness renewable energy sources foreshadowed modern discussions about sustainability and environmental responsibility.
2. The Legacy of Tesla’s Inventions
Tesla’s contributions to science and technology continue to resonate today. His ideas regarding wireless communication paved the way for radio technology and later innovations in wireless networks. Despite facing financial difficulties and skepticism during his lifetime, Tesla’s inventions have become cornerstones of modern electrical engineering and telecommunications.
Tesla’s legacy is celebrated in contemporary culture, inspiring countless engineers and inventors to pursue innovative solutions for the challenges of today. The Tesla name, now synonymous with electric vehicles and renewable energy, serves as a testament to his enduring influence on the future of technology.
B. Marie Curie: The Pioneer of Radioactivity
1. Breaking New Ground in Science
Marie Curie, born Maria Skłodowska in Warsaw, Poland, is renowned for her groundbreaking research on radioactivity. As the first woman to win a Nobel Prize and the only person to win in two different scientific fields (Physics and Chemistry), Curie’s contributions to science are unparalleled. Her discovery of the radioactive elements polonium and radium fundamentally changed the understanding of atomic physics.
Curie’s research laid the foundation for advancements in medical applications of radioactivity, including cancer treatment through radiation therapy. Her relentless pursuit of knowledge and commitment to scientific integrity has inspired generations of scientists, particularly women in STEM fields.
2. Curie’s Enduring Influence on Science
Curie’s legacy extends far beyond her scientific achievements; she has become a symbol of perseverance and dedication in the pursuit of knowledge. Her efforts to promote women in science and her commitment to using scientific discoveries for the betterment of humanity are vital aspects of her legacy.
Today, institutions and awards honoring women in science bear her name, celebrating her impact on the scientific community and promoting diversity in research and innovation. Curie’s pioneering spirit continues to inspire scientists and researchers, urging them to explore the unknown and push the boundaries of knowledge.
C. Johannes Gutenberg: The Father of Printing
1. The Printing Revolution
Johannes Gutenberg, a German inventor, is best known for introducing the printing press to Europe in the 15th century. His invention revolutionized the way information was disseminated, making books more accessible and affordable. The Gutenberg press utilized movable type, allowing for the mass production of written works and significantly contributing to the spread of knowledge during the Renaissance.
The impact of Gutenberg’s printing press on European society was profound. It facilitated the spread of ideas, culture, and literacy, leading to a more informed populace. The rapid dissemination of religious texts, including Martin Luther’s 95 Theses, played a crucial role in the Protestant Reformation, reshaping the religious landscape of Europe.
2. Gutenberg’s Legacy in the Digital Age
Gutenberg’s invention laid the groundwork for the modern publishing industry, influencing everything from literature to journalism. His contributions are seen as pivotal in the transition from the Middle Ages to the modern era, and his legacy continues to shape communication and information sharing today.
In the digital age, the principles established by Gutenberg resonate in the realm of online publishing and digital media. The democratization of information through the internet echoes his vision of making knowledge accessible to all, ensuring that the spirit of innovation and progress continues to thrive.
The contributions of innovators and inventors like Nikola Tesla, Marie Curie, and Johannes Gutenberg have profoundly shaped the course of history and the future of humanity. Their groundbreaking ideas and relentless pursuit of knowledge have not only transformed industries but have also inspired generations to dream big and challenge the status quo. As we reflect on their legacies, we are reminded of the power of creativity and innovation in crafting a better future for all. The spirit of invention continues to drive progress, urging us to embrace new ideas and explore the uncharted territories of science, technology, and human potential.
VI. The Enduring Legacy of Cultural Icons
The contributions of these cultural icons continue to resonate in modern European society, shaping its identity and values. Their works, ideas, and innovations serve as touchstones for current and future generations, reminding us of the power of creativity, thought, and leadership. As we celebrate these figures, we recognize the interconnectedness of art, literature, philosophy, and politics in shaping the cultural landscape of Europe.
We invite you to engage with the accompanying crossword puzzle, where you can test your knowledge of these remarkable cultural icons. Dive deeper into their stories and discover how their legacies continue to inspire us today!
Share to...
I hope you enjoy the content.
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle or article? Subscribe!
You may also be interested in
Share to…
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle?
-
Jigsaw Puzzles
Chinese Zodiac Rabbit Jigsaw Puzzle – Ink Art Series 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Zodiac Watercolor Rooster Puzzle: Artful Elegance 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Autumn Whiskers and Pumpkin Paws Puzzle 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page