Explore & Play
Discover interesting topics and solve the accompanying crossword puzzle.
Bay crossword | Notable Bays Around the World
Table of Contents
To enhance your reading experience, we encourage you to start with the Bay crossword. It offers a fun way to familiarize yourself with key terms and locations related to bays around the world. If you’re not as familiar with the topic, feel free to read the article first for a deeper understanding, then return to the crossword to test your knowledge. Enjoy your journey through the fascinating world of bays!
Bay Crossword
You can either fill in the crossword puzzle directly on this page or click the button in the bottom right corner to print it for free.
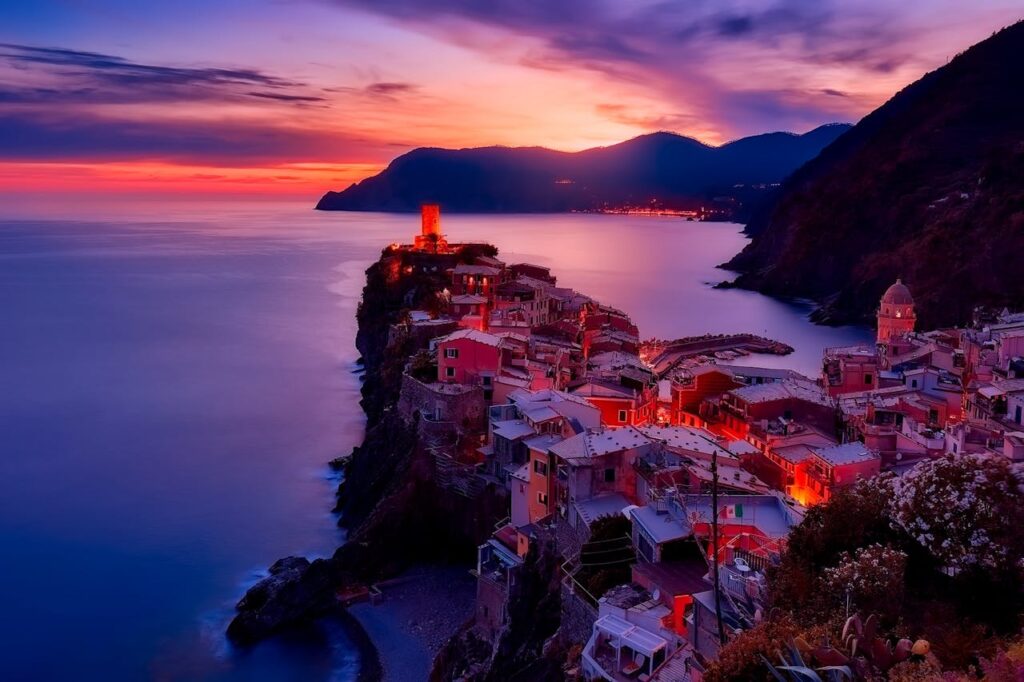

A Comparative Study of Global Bays
Bays are vital geographical features that offer rich ecosystems, cultural significance, and economic opportunities around the world. They serve as natural harbors, support diverse marine life, and play a crucial role in local economies. In this article, we will explore notable bays globally, highlighting their unique characteristics and importance. As you read, you might enjoy solving the accompanying crossword puzzle that features many of these remarkable bays.
1. The Definition and Formation of Bays
Understanding what constitutes a bay is crucial for appreciating the diversity of these natural formations. A bay is typically defined as a body of water partially surrounded by land and often connected to an ocean or sea. These geographical features can be formed through various processes, including erosion, sediment deposition, and glacial activity. For instance, tectonic shifts can create unique shapes and sizes, resulting in distinct ecosystems. Consequently, each bay develops its own character, influenced by its surrounding environment.
2. Notable Bays Around the World
From bustling ports to serene landscapes, the world’s bays each have their unique charm and significance. These natural harbors are more than just geographical features; they are vital to the economies, ecosystems, and cultures of the regions they inhabit. Let’s delve deeper into some of the most notable bays around the globe.
2.1 San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is renowned for its iconic Golden Gate Bridge, which offers breathtaking views of both the bay and the city. The bay itself is a natural harbor that has been pivotal in California’s history, serving as a major entry point for immigrants and goods. Its waters are home to a diverse array of marine life, including various fish species, sea lions, and migratory birds. The bay’s surrounding wetlands are essential for wildlife and serve as important buffers against rising sea levels. Additionally, numerous recreational activities, such as kayaking, sailing, and birdwatching, attract both locals and tourists alike, making San Francisco Bay a vibrant hub of activity.
2.2 Chesapeake Bay
Chesapeake Bay, the largest estuary in the United States, is a critical resource for the region, known for its rich biodiversity and historical significance. The bay’s waters are a habitat for a plethora of marine life, including blue crabs, oysters, and rockfish. Its historical importance dates back to colonial times when it served as a major site for trade and agriculture. However, the bay faces environmental challenges, including pollution from agricultural runoff and urban development. Efforts to restore its health have been implemented, focusing on improving water quality and habitat restoration. The bay also supports a variety of recreational activities, from fishing to boating, making it a cherished destination for many.
2.3 Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay is significant both geographically and historically, acting as a key route for early explorers and traders. This vast body of water, surrounded by rugged wilderness, is home to unique wildlife, including polar bears, beluga whales, and migratory birds. The bay continues to be essential for the indigenous communities that rely on its resources for sustenance and cultural practices. In recent years, Hudson Bay has gained attention for its rich natural resources, including minerals and fish, which are increasingly being explored. The bay’s stunning landscapes and abundant wildlife make it a captivating area for nature lovers and researchers alike.
2.4 Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay, situated between Spain and France, is famous for its dramatic coastline and unpredictable weather. Known for its rich marine biodiversity, the bay’s deep waters are home to numerous fish species, making it a hotspot for commercial and recreational fishing. The coastal towns surrounding the bay, such as Biarritz and San Sebastián, are popular tourist destinations, known for their beautiful beaches and vibrant culture. The bay also serves as a critical habitat for marine mammals, including dolphins and whales, with various conservation initiatives focused on protecting these species and their environments.
2.5 Tokyo Bay
Tokyo Bay is a bustling hub surrounding Japan’s capital, vital for transportation and commerce. This busy waterway has been transformed into a metropolitan area, featuring a blend of modern architecture and traditional landscapes. The bay is a vital shipping route, supporting Japan’s economy through trade and tourism. Despite its urbanization, Tokyo Bay is home to diverse marine species, and efforts are underway to protect its ecosystems. The waterfront area offers numerous recreational activities, from parks to waterfront promenades, making it a vibrant destination for both locals and visitors.
2.6 Guanabara Bay
Guanabara Bay is renowned for its stunning views of Sugarloaf Mountain and the vibrant city of Rio de Janeiro. As one of Brazil’s most important economic hubs, the bay supports tourism, shipping, and fishing industries. Its historical significance is marked by numerous cultural landmarks, festivals, and events that attract visitors from all over the world. However, Guanabara Bay faces environmental challenges, including pollution and habitat loss. Conservation efforts are ongoing, aiming to restore the bay’s natural beauty and biodiversity while promoting sustainable practices in the surrounding areas.
2.7 Tampa Bay
Tampa Bay, located in Florida, is celebrated for its lively port and rich marine ecosystem. The bay supports a variety of recreational activities, such as fishing, boating, and wildlife viewing, contributing significantly to the local economy. Its diverse habitats, including mangroves and seagrass beds, are crucial for various marine species. The bay is also home to vibrant coastal communities that benefit from its resources. Local initiatives focus on preserving the bay’s ecosystems while promoting sustainable tourism and recreational opportunities.
2.8 Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor has deep historical roots, dating back to the American Revolution, and remains a vital part of the city’s identity. Today, it is a bustling port that offers a range of recreational activities, including sailing, kayaking, and whale watching. The harbor encompasses several islands, each with unique attractions, from hiking trails to historic sites. Conservation efforts aim to improve water quality and protect the harbor’s ecosystems, ensuring that it continues to serve both the local community and visitors.
2.9 Narragansett Bay
Narragansett Bay is known for its stunning coastal scenery and rich marine life. It serves as a vital resource for fishing and tourism, drawing visitors to its beaches and recreational opportunities. The bay’s diverse ecosystems support a wide variety of wildlife, including shellfish and seabirds. Local initiatives focus on protecting the bay’s habitats and promoting sustainable practices among fishermen and tourists, ensuring that Narragansett Bay remains a treasured destination for generations to come.
2.10 Moreton Bay
Moreton Bay, located in Queensland, Australia, is famous for its beautiful marine parks and rich biodiversity. This bay attracts nature enthusiasts and tourists alike, offering opportunities for activities such as snorkeling, fishing, and kayaking. Its waters are home to various marine species, including dugongs, dolphins, and colorful coral reefs. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these ecosystems and promote eco-friendly tourism practices, ensuring the preservation of Moreton Bay’s natural beauty for future generations.
3. Unique Features of Specific Bays
Each bay possesses unique features that make them stand out in their respective regions, showcasing the diverse beauty and ecological importance of these natural wonders.
3.1 Bay of Islands
The Bay of Islands in New Zealand is a breathtakingly scenic destination, featuring over 140 islands that offer a myriad of experiences. Known for its stunning landscapes, this bay is popular for water sports, including kayaking and sailing, as well as fishing. The rich marine life, including dolphins and whales, enhances its appeal, making it a hotspot for eco-tourism. The area is also steeped in Maori culture, with numerous historical sites that provide insight into the region’s heritage.
3.2 Kotor Bay
Kotor Bay, characterized by its fjord-like qualities, is a UNESCO World Heritage site renowned for its dramatic landscapes and rich history. Surrounded by towering mountains and dotted with charming medieval towns, the bay offers visitors a glimpse into the past. Its crystal-clear waters are perfect for sailing and swimming, while the picturesque scenery provides countless opportunities for photography. Kotor Bay is also known for its vibrant cultural events, including music festivals and local markets, making it a dynamic destination.
3.3 Bay of Naples
The Bay of Naples is celebrated for its striking coastline and vibrant cultural scene. The bay is home to stunning archaeological sites, including Pompeii and Herculaneum, which draw history buffs from around the globe. Charming seaside towns, such as Positano and Sorrento, offer visitors a taste of local cuisine and culture. The bay’s natural beauty is complemented by opportunities for outdoor activities, including hiking on the nearby Amalfi Coast and exploring the islands of Capri and Ischia.
3.4 King George Sound
King George Sound, located in Western Australia, is historically significant for early explorers and offers a wealth of natural beauty. The bay features pristine beaches and diverse ecosystems, making it an ideal location for marine activities like fishing, diving, and whale watching. The area is rich in wildlife, with opportunities to spot seals, dolphins, and various bird species. King George Sound also holds cultural significance for local indigenous communities, who have inhabited the region for thousands of years.
3.5 Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy is famous for having the highest tides in the world, a natural phenomenon that creates unique ecosystems. The dramatic tidal fluctuations expose vast areas of mudflats, which are essential feeding grounds for migratory birds and marine species. The bay is also known for its stunning coastal cliffs and picturesque landscapes, attracting visitors for hiking and whale watching. Ongoing research and conservation efforts aim to protect the bay’s ecosystems and promote sustainable tourism practices, ensuring the continued health of this remarkable natural wonder.
4. The Role of Bays in Economic Activities
Bays serve as critical hubs for various economic activities, significantly impacting local and regional economies. Their natural characteristics provide numerous opportunities for industries such as shipping, fishing, tourism, and recreation. Understanding the multifaceted roles of bays in economic activities highlights their importance to communities worldwide.
4.1 Shipping and Trade
Many bays, such as San Francisco Bay and Tampa Bay, are vital for shipping and trade. Their natural harbors provide sheltered areas for large vessels, allowing for safe docking and efficient loading and unloading of goods. These locations often develop into major ports that facilitate international trade, connecting regions and countries. The presence of nearby infrastructure, such as roads and railways, enhances access to these ports, promoting commerce and economic growth. Ports located in bays also create jobs, from shipping and logistics to customs and security, significantly benefiting local economies.
4.2 Fishing Industries
Bays are essential for fishing industries, providing rich marine ecosystems that support diverse fish populations. Areas like Chesapeake Bay are famous for their seafood, including blue crabs and oysters, which are economically important to local communities. Fishing contributes not only to local diets but also to regional economies through job creation in fishing, processing, and distribution. Sustainable fishing practices are crucial for maintaining healthy fish populations and ecosystems, ensuring that these economic benefits can continue for future generations.
4.3 Tourism and Recreation
The natural beauty and recreational opportunities offered by bays attract millions of tourists each year. Bays like the Bay of Naples and Moreton Bay are known for their stunning landscapes, water sports, and wildlife, making them popular destinations for visitors. Tourism generates substantial revenue, supporting local businesses such as hotels, restaurants, and recreational equipment rentals. Additionally, recreational activities like boating, fishing, and wildlife watching foster a connection between communities and their natural environments, promoting conservation efforts.
4.4 Real Estate and Development
Bays also influence real estate development, particularly in coastal areas. Waterfront properties often command higher prices due to their desirable views and access to recreational activities. This demand can drive urban development and revitalization, enhancing local infrastructure and amenities. However, careful planning is essential to balance development with environmental preservation, ensuring that the economic benefits do not come at the expense of natural ecosystems.
5. Environmental Considerations
While bays play vital roles in economic activities, they are also susceptible to various environmental challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of these ecosystems and the livelihoods they support.
5.1 Pollution and Water Quality
One of the most pressing environmental issues facing bays is pollution. Agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban development can introduce harmful substances into the water, degrading water quality and harming marine life. For example, Chesapeake Bay has struggled with nutrient pollution, leading to algal blooms that deplete oxygen levels and create dead zones. Efforts to improve water quality include implementing stricter regulations, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and restoring wetlands that can filter pollutants.
5.2 Habitat Loss and Conservation
Urbanization and industrial activities can lead to habitat loss, threatening the delicate ecosystems within bays. Wetlands, mangroves, and seagrass beds are essential for providing shelter and breeding grounds for various species. Conservation initiatives aimed at protecting these habitats are critical for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem health. Organizations and governments often collaborate on restoration projects to rehabilitate damaged areas, enhance wildlife habitats, and improve overall ecological resilience.
5.3 Climate Change Impacts
Bays are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, and changes in water temperature. These changes can disrupt local ecosystems, alter fish migration patterns, and exacerbate flooding in coastal communities. Adaptive management strategies are essential for mitigating these impacts, such as implementing sustainable coastal development practices, enhancing flood defenses, and promoting ecosystem-based approaches to conservation.
5.4 Balancing Economic Growth and Environmental Protection
Finding a balance between economic growth and environmental protection is crucial for the sustainability of bays. Policymakers, businesses, and communities must work together to develop integrated management plans that prioritize both economic activities and ecological health. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts and promoting sustainable practices can create a sense of stewardship, ensuring that the benefits of bays can be enjoyed by future generations without compromising their integrity.
6. Cultural Significance and Festivals
Bays are not only vital for their economic and ecological roles but also hold significant cultural importance for the communities that surround them. They often serve as focal points for traditions, celebrations, and local identity, enriching the cultural tapestry of their regions.
6.1 Historical and Cultural Heritage
Many bays have deep historical roots that reflect the stories of the communities that have inhabited their shores. For example, Boston Harbor is steeped in American history, serving as a backdrop for pivotal events such as the Boston Tea Party. Similarly, Hudson Bay was central to the fur trade and exploration, shaping the interactions between indigenous peoples and European settlers. These historical connections foster a sense of identity and belonging among local populations.
6.2 Festivals Celebrating Coastal Life
Bays are often celebrated through festivals that highlight local culture, traditions, and marine heritage. Events such as the Chesapeake Bay Seafood Festival in Virginia celebrate the region’s fishing culture, showcasing local seafood, arts, and crafts. These festivals not only promote local businesses but also educate the public about sustainable practices and the importance of preserving marine resources.
In New Zealand, the Bay of Islands is famous for its annual music festival, which attracts visitors and artists from around the world. This event highlights the region’s vibrant culture while promoting tourism and community engagement. Such festivals create opportunities for local artisans and performers, fostering pride in cultural heritage.
6.3 Community Connections and Environmental Awareness
Cultural events centered around bays often incorporate themes of environmental stewardship and conservation. Many festivals include educational components that raise awareness about local ecosystems and the challenges they face. Engaging the community in these discussions fosters a deeper understanding of the importance of protecting natural resources. Events like beach clean-ups and conservation workshops are often integrated into festival activities, empowering attendees to take action.
7. Future Challenges and Conservation Efforts
As vital ecosystems, bays face numerous future challenges that threaten their health and sustainability. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated conservation efforts, innovative solutions, and active community involvement.
7.1 Impact of Climate Change
Climate change poses significant threats to bays, including rising sea levels, increased storm frequency and intensity, and shifting ecosystems. These changes can lead to habitat loss, increased salinity, and altered species distributions, all of which disrupt the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. Addressing climate change requires comprehensive strategies, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing coastal resilience through habitat restoration and sustainable development practices.
7.2 Pollution Control and Water Quality Management
Pollution continues to be a major challenge for many bays. Urban runoff, agricultural practices, and industrial discharges contribute to declining water quality and harm marine life. Effective pollution control measures are essential for protecting these ecosystems. Implementing stricter regulations, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and increasing public awareness about pollution prevention can significantly improve water quality in bays.
7.3 Habitat Restoration and Biodiversity Protection
Efforts to restore habitats, such as wetlands and seagrass beds, are crucial for enhancing the resilience of bay ecosystems. These areas serve as nurseries for fish and provide essential services, including flood protection and water filtration. Conservation organizations and governments often collaborate on restoration projects that aim to rehabilitate degraded habitats, ensuring that biodiversity is protected for future generations.
7.4 Community Engagement and Education
Active community involvement is vital for the success of conservation efforts. Engaging local populations in decision-making processes, educational programs, and volunteer opportunities fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for the health of their bays. Schools, non-profit organizations, and local governments can work together to create programs that educate the public about the importance of conservation and sustainable practices, inspiring future generations to continue these efforts.
7.5 Policy Development and Sustainable Management
Developing effective policies for bay management requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and community organizations. Integrated management approaches that consider economic, environmental, and social factors are essential for promoting sustainable practices. Policymakers must prioritize the long-term health of bay ecosystems while supporting economic activities that do not compromise environmental integrity.
Preserving Our Bays for Future Generations
The diversity of bays around the world highlights their ecological, cultural, and economic significance, making their preservation essential for future generations. As we continue to explore and celebrate these natural wonders, it’s vital to remember our role in protecting them. By promoting conservation efforts and supporting local initiatives, we can ensure that these bays remain vibrant ecosystems for years to come.
We invite you to engage with the accompanying crossword puzzle, which features many of the bays discussed in this article. Challenge yourself to learn more about these remarkable locations and their significance!
Share to...
I hope you enjoy the content.
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle or article? Subscribe!
You may also be interested in
Share to…
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle?
-
Jigsaw Puzzles
Chinese Zodiac Serpent Watercolor Jigsaw Puzzle 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Zodiac Watercolor Rooster Puzzle: Artful Elegance 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Lofoten Serenity: Abstract Puzzle 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page