Explore & Play
Discover interesting topics and solve the accompanying crossword puzzle.
Ancient City Crossword | Exploration of Historical Legacies
Table of Contents
Welcome to our exploration of ancient cities! To enhance your experience, we invite you to start by tackling the Ancient City Crossword at the beginning of this post. This will challenge your knowledge and set the stage for our in-depth article. If you’re less familiar with the topic, feel free to dive into the article first to build your understanding, and then come back to the crossword for a fun review. Enjoy the journey through history!
Ancient City Crossword
You can either fill in the crossword puzzle directly on this page or click the button in the bottom right corner to print it for free.
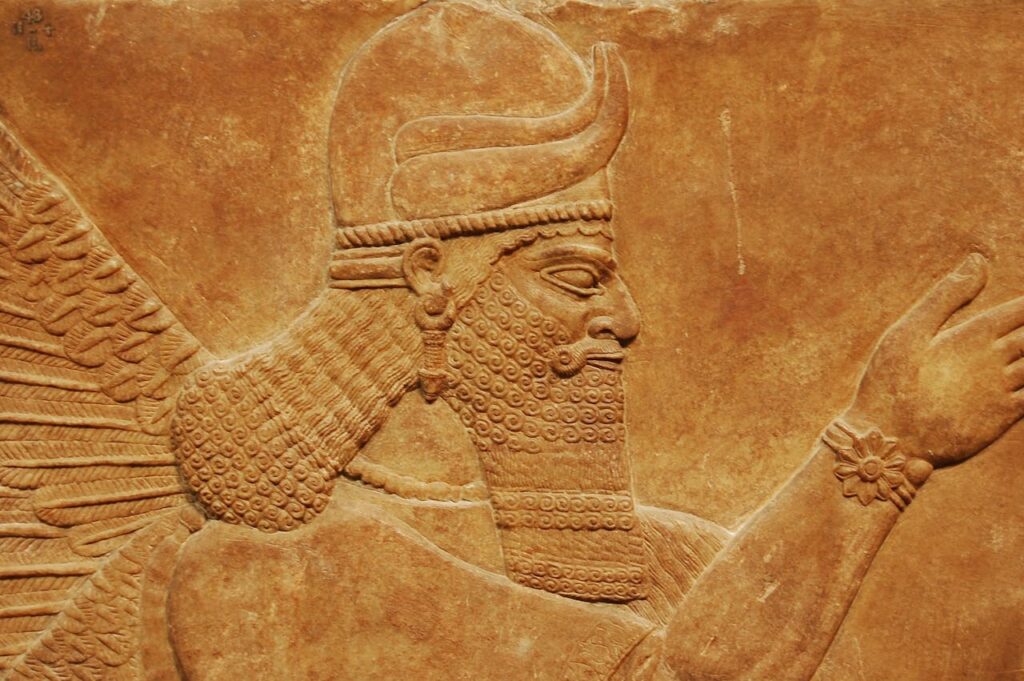

Journey Through Time: Exploring the Most Influential Ancient Cities and Their Legacies
Throughout history, cities have been the beating heart of civilizations, serving as centers of power, culture, and innovation. Join us as we journey through some of the most influential ancient cities and uncover their legacies. To further engage with this fascinating topic, we invite you to test your knowledge with our ancient cities crossword puzzle, which includes many of the cities discussed here.
1. The Cradle of Civilization: Mesopotamia
1.1 Babylon: The Jewel of Mesopotamia
Babylon, often referred to as the jewel of Mesopotamia, stood as a beacon of culture and grandeur in ancient times. Located in present-day Iraq, this city was renowned for its stunning architectural achievements, including the famed Hanging Gardens, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The city’s impressive ziggurats and the Ishtar Gate highlighted Babylon’s grandeur and its pivotal role in Mesopotamian culture. As the center of a powerful empire, Babylon influenced many aspects of Mesopotamian society, from governance to religion.
1.2 Ur: Gateway to Ancient Sumer
As one of the earliest and most significant cities of ancient Sumer, Ur played a crucial role in the development of early urban society. Situated near the Persian Gulf, Ur was a major center for trade and culture. It is famous for its well-preserved ziggurat and royal tombs, which provide valuable insights into Sumerian art and religion. Ur was also a pioneering force in the development of writing, with its cuneiform script marking a significant leap in human communication and administration.
1.3 Nineveh: The Majestic Assyrian Capital
Nineveh, the illustrious capital of the Assyrian Empire, was renowned for its architectural marvels and cultural achievements. Located near modern-day Mosul, Iraq, Nineveh was an impressive city with grand palaces, massive walls, and the renowned library of Ashurbanipal. This library housed a vast collection of texts, including some of the earliest known works of literature and science. Nineveh’s contributions to Assyrian culture and its role in historical records make it a key city in understanding ancient Mesopotamian civilization.
2. The Ancient Egyptian Legacy
2.1 Memphis: The Ancient City of the Pyramids
Memphis, with its strategic location near the great pyramids, was a cornerstone of ancient Egyptian civilization. As one of Egypt’s oldest capitals, Memphis served as a major religious and administrative center. Its proximity to the pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx highlights its significance in early Egyptian culture. The city was home to many temples dedicated to gods such as Ptah, reflecting its importance in religious practices and state affairs.
2.2 Thebes: The City of Temples and Tombs
Thebes, known for its grand temples and royal tombs, was a major religious and political center in ancient Egypt. Located on the eastern bank of the Nile, Thebes was the site of the famous Karnak and Luxor temples, which were central to Egyptian worship and ceremonies. The city’s Valley of the Kings, where many pharaohs were buried, showcases Thebes’ role in funerary practices and its artistic achievements. Thebes’ temples and tombs offer a glimpse into Egypt’s religious life and the grandeur of its rulers.
2.3 Heliopolis: The Sun God’s Domain
Heliopolis, dedicated to the sun god Ra, was a vital center of worship and learning in ancient Egypt. Situated near modern Cairo, Heliopolis was renowned for its great temple dedicated to Ra and its contributions to Egyptian religion and astronomy. The city’s scholars made significant advancements in understanding the cosmos, which influenced later scientific thought. Heliopolis’ role in Egyptian mythology and its impact on religious practices make it a key site in ancient history.
3. The Greek City-States: Cradles of Western Civilization
3.1 Athens: The Birthplace of Democracy
Athens, celebrated as the birthplace of democracy and philosophy, has left an indelible mark on Western thought. Located in Greece, Athens was the epicenter of political and intellectual activity during the 5th century BCE. The city was home to great philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, whose ideas continue to influence modern philosophy. Athens’ development of democratic principles and its contributions to arts and sciences underscore its significance in shaping Western civilization.
3.2 Sparta: The Warrior Society
In contrast to Athens, Sparta was known for its military discipline and warrior society. Situated in the region of Laconia, Sparta was a city-state renowned for its rigorous training of soldiers and its unique social structure. Spartan society was focused on military excellence and communal living, which contributed to its reputation as a formidable military power. The city’s emphasis on discipline and strength made it a key player in ancient Greek politics and warfare.
3.3 Mycenae: Echoes of Homer’s Epics
Mycenae, immortalized in Homer’s epics, was a prominent center of Greek civilization during the late Bronze Age. Located in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula, Mycenae was known for its impressive architectural structures, including the Lion Gate and the Treasury of Atreus. The city’s role in Greek mythology and its archaeological findings provide valuable insights into early Greek society and its legendary heroes.
4. The Phoenician Powerhouses
4.1 Carthage: The Rival of Rome
Carthage, a formidable Phoenician city-state, was a major rival to Rome in the ancient Mediterranean world. Located in present-day Tunisia, Carthage was a powerful maritime and commercial center known for its naval prowess and extensive trade networks. The city’s conflicts with Rome, particularly during the Punic Wars, highlight its strategic importance and its impact on Mediterranean politics.
4.2 Tyre and Sidon: The Twin Capitals of Phoenician Trade
Tyre and Sidon, two of the most important Phoenician cities, were renowned for their maritime trade and industry. Both cities, located in modern-day Lebanon, were major centers of commerce and culture. Tyre was famous for its production of purple dye, while Sidon was known for its skilled craftsmanship and trade networks. The cities’ contributions to Phoenician culture and their role in ancient trade highlight their significance in the ancient world.
4.3 Byblos: The Birthplace of the Alphabet
Byblos, one of the oldest Phoenician cities, is credited with the development of one of the earliest alphabets. Situated along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Lebanon, Byblos was a key center for trade and cultural exchange. The city’s contributions to writing and its role in the dissemination of the alphabet underscore its importance in the history of communication.
5. The Ancient Near East and Beyond
5.1 Persepolis: The Persian Empire’s Ceremonial Capital
Persepolis, the ceremonial capital of the Persian Empire, was a symbol of Persian grandeur and architectural innovation. Located in present-day Iran, Persepolis was renowned for its magnificent palaces, monumental staircases, and detailed bas-reliefs. The city’s role as a ceremonial center and its architectural achievements reflect the splendor of the Persian Empire and its cultural achievements.
5.2 Uruk: The Dawn of Urban Civilization
Uruk, one of the first major cities in history, played a pivotal role in the early development of urban society and writing. Situated in ancient Mesopotamia, Uruk was a center of innovation and culture, known for its advanced urban planning and early cuneiform writing. The city’s contributions to urbanization and its role in the development of writing systems highlight its significance in ancient history.
5.3 Hattusa: The Hittite Empire’s Stronghold
Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Empire, was a key player in the ancient Near East’s political landscape. Located in modern-day Turkey, Hattusa was known for its impressive fortifications and monumental architecture. The city’s role in Hittite politics and its archaeological remains provide valuable insights into the Hittite Empire and its interactions with neighboring civilizations.
6. The Cities of the Silk Road
6.1 Samarkand and Bukhara: Crossroads of the Silk Road
Samarkand and Bukhara, two pivotal cities along the Silk Road, served as major centers of trade and cultural exchange. Located in present-day Uzbekistan, both cities were crucial hubs for merchants and travelers moving between East and West. Their vibrant markets, rich cultural heritage, and architectural landmarks reflect their significance in facilitating cross-cultural interactions.
6.2 Merv: A Hub of Silk Road Activity
Merv, strategically located on the Silk Road, was a bustling hub of commerce and cultural interaction. Situated in present-day Turkmenistan, Merv was known for its vibrant trade activities and its role as a melting pot of diverse cultures. The city’s importance in the Silk Road network underscores its impact on trade and cultural exchange.
7. The New World Wonders
7.1 Teotihuacan: The Mysteries of the Pyramid of the Sun
Teotihuacan, renowned for the Pyramid of the Sun, remains one of the most mysterious and awe-inspiring ancient cities in Mesoamerica. Located in present-day Mexico, Teotihuacan was a major urban center with impressive pyramids, temples, and avenues. The city’s architectural achievements and its influence on later Mesoamerican cultures make it a key site in understanding ancient civilizations.
7.2 Chichen Itza: The Maya’s Architectural Triumph
Chichen Itza, with its iconic Temple of Kukulcán, stands as a testament to the Maya civilization’s architectural prowess. Situated in the Yucatán Peninsula,
Share to...
I hope you enjoy the content.
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle or article? Subscribe!
You may also be interested in
Share to…
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle?
-
Jigsaw Puzzles
Twelve Zodiac Mice Ink Wash Jigsaw Puzzle 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Zodiac Ink Art Puzzle: The Playful Monkey 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Autumn Whiskers and Pumpkin Paws Puzzle 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page