Explore & Play
Discover interesting topics and solve the accompanying crossword puzzle.
Source crossword | Earth’s Vital Energy Sources
Table of Contents
At the beginning of this blog post, you can choose to start with the Source crossword to test your knowledge about Earth’s energy sources, or if you’re not yet familiar with the topic, you can first read the article to gain more insights and then return to the crossword. Both approaches will help you engage with the content in a way that suits your preferences.
Source Crossword
You can either fill in the crossword puzzle directly on this page or click the button in the bottom right corner to print it for free.
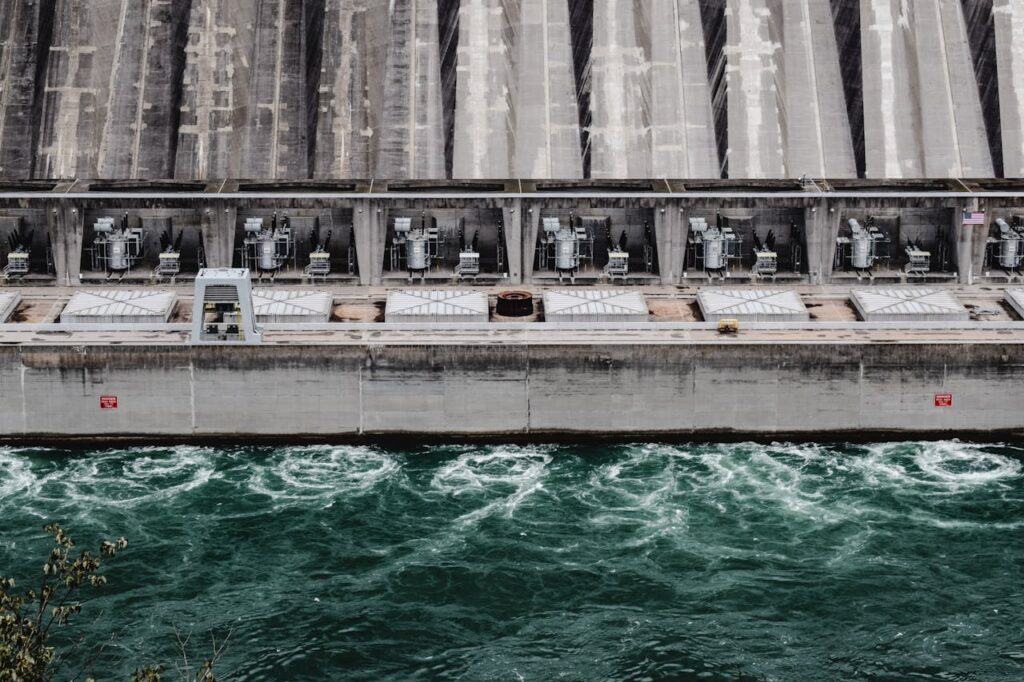

The Power of the Earth: From Energy Sources to Natural Wonders
Introduction: The Earth as a Source of Life and Energy
From the air we breathe to the electricity that powers our homes, the Earth provides an abundance of resources that sustain life and fuel our technological advancements. Every day, we depend on nature’s power in various forms—whether it’s the sunlight that warms us or the rivers that power hydroelectric plants. The planet’s abundant natural resources have been at the heart of human progress, but as we move forward, the challenge lies in managing these resources responsibly. This article will explore the Earth’s vast sources of energy, from natural wonders to human-made resources, and how we harness them for sustainable living.
Section 1: Understanding Natural Energy Sources
1.1 The Vital Role of Water: Rivers, Springs, and Lakes
Water, in its many forms, has long been a source of life, power, and nourishment on Earth. Rivers, springs, and lakes are integral parts of the water cycle, providing us with fresh water for drinking, agriculture, and industry. Rivers like the Amazon and the Nile not only sustain life but also power hydroelectric plants that generate a significant portion of the world’s electricity. Springs, which are natural sources of groundwater, feed many communities with clean, fresh water. Lakes, large bodies of water, serve as storage for these resources, as well as crucial habitats for wildlife.
In addition to their vital role in the water cycle, these water sources also hold economic value. Many countries rely on rivers and lakes for irrigation, which in turn supports agricultural industries. The energy derived from water through hydropower is one of the oldest forms of renewable energy, and today, it continues to provide an essential part of the world’s electricity generation.
1.2 The Power of the Sun: Harnessing Solar Energy
Solar energy, one of the most abundant and sustainable sources of power, has been used by humans for centuries in various forms. The sun’s energy fuels photosynthesis, which allows plants to grow and produce food. Solar energy is also harnessed through solar panels, which capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This renewable source of power has gained tremendous popularity as a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels.
In recent years, technological advancements have made solar energy more efficient and accessible, with solar farms popping up across the globe. The potential for solar energy is vast, especially in regions with high levels of sunlight, such as the Middle East and parts of Africa. Solar power is expected to play a crucial role in combating climate change, as it produces no harmful emissions when used.
1.3 Wind and Water: Unseen Forces of Nature
Wind and water, though invisible, are two of the most powerful forces of nature, harnessed for centuries to power our world. Wind energy is captured by wind turbines, which convert the kinetic energy of moving air into electricity. Wind farms, often located in coastal regions or open plains, have become an increasingly common sight in the renewable energy landscape.
Similarly, water currents in oceans and rivers have been used for centuries in the form of watermills and tidal power. Tidal energy, generated by the movement of the tides, is a growing field in renewable energy development. Both wind and water offer sustainable, clean alternatives to fossil fuel-based energy, and they continue to play a significant role in the global energy mix.
1.4 Forests and Trees: Nature’s Renewable Resource
Forests are not just scenic landscapes—they are critical sources of oxygen, wood, and biodiversity that support life on Earth. Trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contributing to the global balance of gases in the atmosphere. They also provide habitats for countless species of animals, birds, and insects, making them essential to the planet’s biodiversity.
Wood from trees has been used for centuries as a building material, fuel, and even in the creation of paper. However, with the rise of deforestation, it’s crucial to focus on sustainable forestry practices to ensure that forests remain a renewable resource. Replanting trees and using wood responsibly can help preserve this vital natural resource for future generations.
Section 2: Earth’s Geological Wonders: Mountains, Volcanoes, and More
2.1 Mountains: Sources of Minerals, Water, and Beauty
Mountains, majestic and powerful, are more than just natural wonders—they are vital sources of water, minerals, and biodiversity. The snow that caps many mountain ranges slowly melts and feeds rivers and lakes, providing fresh water to surrounding areas. Mountains are also rich in minerals, such as gold, silver, and coal, which have been mined for centuries and played an essential role in industrial development.
Beyond their resource value, mountains hold great cultural and spiritual significance for many people around the world. They serve as symbols of strength and resilience and provide stunning landscapes that attract tourists and nature lovers alike.
2.2 Volcanoes: Earth’s Fiery Energy Source
Volcanoes, while often feared for their destructive power, are also a source of geothermal energy and rich volcanic soil. Geothermal energy, which is derived from the heat of the Earth’s core, is used to generate electricity in many volcanic regions. Countries like Iceland and New Zealand are pioneers in harnessing geothermal power, which provides a sustainable, clean energy source.
Volcanic soil is also incredibly fertile, allowing for the growth of crops in regions around active volcanoes. The minerals found in the soil are essential for plant growth, making these areas ideal for agriculture. Despite the dangers posed by volcanoes, they remain one of Earth’s most productive sources of energy and natural resources.
2.3 The Earth’s Inner Power: Geothermal Energy
Beneath the Earth’s surface lies a nearly limitless source of energy—geothermal energy. This form of energy is derived from the heat stored within the Earth’s crust and can be harnessed through geothermal power plants. Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal energy produces little to no greenhouse gas emissions, making it a clean and sustainable alternative.
Geothermal power has the potential to provide a constant and reliable source of energy, unlike solar and wind power, which depend on weather conditions. However, geothermal energy is geographically limited to areas with volcanic activity or tectonic plate movement, making its global availability uneven.
Section 3: Human-Made Sources of Energy
3.1 Fossil Fuels: The Era of Coal, Oil, and Gas
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, have been the driving force behind industrialization for over a century. These energy sources have powered factories, homes, and transportation, playing a central role in the economic development of many countries. However, the extraction and use of fossil fuels come with significant environmental consequences, such as air pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction.
The depletion of fossil fuel reserves has also raised concerns about energy security. As the world shifts toward more sustainable alternatives, the future of fossil fuels remains uncertain. However, many countries continue to rely on these energy sources, making the transition to renewables a complex and long-term process.
3.2 The Rise of Nuclear Energy: A Source of Controversy
Nuclear energy, though powerful, remains a topic of debate due to concerns over safety and waste disposal. Nuclear power plants use uranium and other radioactive elements to generate heat, which is then used to produce electricity. While nuclear energy is a low-emission source of power, accidents like the Fukushima disaster and Chernobyl have raised serious concerns about its safety.
Despite these challenges, nuclear energy continues to be seen as a necessary alternative to fossil fuels, particularly in countries seeking to reduce their carbon emissions. The development of safer nuclear technologies and better waste management systems is key to ensuring that nuclear power can play a role in the clean energy future.
Section 4: The Role of Information: Knowledge as a Source
4.1 Books, Libraries, and the Transmission of Knowledge
Books and libraries have long been sources of knowledge, preserving humanity’s collective wisdom for future generations. Libraries are sanctuaries of information, where knowledge is stored and made accessible to anyone seeking it. From ancient manuscripts to modern scientific texts, books have allowed us to pass on essential information about everything from energy sources to the natural world.
Libraries continue to serve as a foundation for learning in today’s digital age. Even though information is increasingly found online, libraries remain vital resources for research, education, and community engagement.
4.2 The Internet and Digital Sources: The Modern Era of Information
In the digital age, the internet has become the ultimate source of information, shaping how we learn, communicate, and live. Search engines, online databases, and academic journals provide instant access to knowledge about virtually every topic imaginable, including energy sources, sustainability, and the environment. The internet is a key driver in the dissemination of information about renewable energy and the challenges facing the planet.
The rise of social media and blogs has also revolutionized the way we engage with information. Podcasts and online discussions allow people to share their insights and experiences, fostering a global conversation about environmental issues and solutions.
4.3 Research and Data: Scientific Exploration and Discovery
Research and data are at the heart of discovery, providing insight into everything from space exploration to climate change. Scientists rely on data to understand the Earth’s resources, the impact of human activity, and how we can mitigate environmental challenges. The findings from research shape public policy, guide technological development, and help individuals make informed decisions about energy use.
Data-driven research is particularly important in the field of climate science, where understanding the Earth’s changing ecosystems is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat global warming. Ongoing studies continue to highlight the urgency of shifting toward sustainable energy sources and protecting the planet’s natural resources.
Section 5: The Future of Energy: Sustainable Sources and Innovation
5.1 Renewable Energy: Wind, Solar, and Hydropower
Renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Wind and solar power, in particular, have seen a dramatic increase in investment and technological advancements, making them more efficient and cost-effective. Hydropower, with its ability to generate electricity from flowing water, remains one of the most reliable and mature forms of renewable energy.
As countries and industries continue to invest in renewable energy infrastructure, the transition to a cleaner, greener energy future becomes increasingly viable. Innovations in energy storage technologies and smart grids will further enhance the efficiency and reliability of renewable sources.
5.2 The Role of Innovation in Clean Energy Solutions
Innovation is key to unlocking the potential of clean energy sources. Breakthroughs in energy storage, like batteries that can store solar and wind power for later use, will allow for a more reliable energy grid. Additionally, advancements in energy efficiency, carbon capture technologies, and nuclear fusion could revolutionize the way we generate and use energy.
The future of clean energy depends on the collaboration between governments, industries, and individuals to invest in new technologies and policies that promote sustainability. It will require global cooperation to address the challenges of climate change and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Earth’s Energy for a Sustainable Future
The Earth is a vast, dynamic system of interconnected resources that power life, industry, and progress. By understanding and utilizing its energy sources, from water and wind to solar and geothermal power, we can create a more sustainable future. However, this will require conscious effort, innovation, and cooperation across all sectors of society. As we move forward, it is essential to focus on reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and embracing clean, renewable energy solutions.
Let’s take action by learning more and understanding how we can contribute to a sustainable future. Try the crossword puzzle related to these energy sources and discover more about how the Earth powers our lives!
Share to...
I hope you enjoy the content.
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle or article? Subscribe!
You may also be interested in
Share to…
Want to receive our daily crossword puzzle?
-
Jigsaw Puzzles
Zodiac Ink Dog Puzzle: Artful Elegance 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Rose-Tinted Dreams Floral Puzzle 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Jigsaw Puzzles
Zodiac Watercolor Rooster Puzzle: Artful Elegance 250 | 300 | 500 Pieces
kr 348,00 – kr 439,00Price range: kr 348,00 through kr 439,00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page